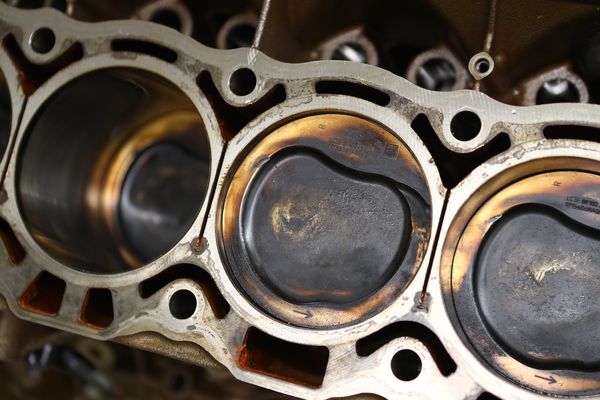
Ford 7.3 Gas Cylinder Numbers (Godzilla Firing Order)
Don’t be surprised when you get more than one answer to this firing order question. Some people may think they know the answer and simply say it like they are an expert. Make sure to double check as Ford made the Powerstroke and the Godzilla at 7.3L
The Godzilla firing order is said to be 1-5-4-8-6-3-7-2 and we checked different websites to confirm that firing order. The Powerstroke is listed at 1-2-7-3-4-5-6-8. Again, we checked more than one website that talks about this engine.
To learn more about the firing orders of the Powerstroke and possibly the Godzilla engines, just continue to read our article. It brings as much information as possible to the discussion. Keep reading to get the important information.
How Many Cylinders Are in a 7.3 Powerstroke?

The Powerstroke motor comes with 8 cylinders in a cast iron block. There are 6 head bolts per cylinder and the pistons were made from cast aluminum. The design was an OHV with 2 valves per cylinder as well as hydraulic lifters.
The horsep[ower changed over the years. When the Powerstroke first came out in 1994 it was given 210 HP, then from 1996 on up, the HP changed. That year saw the engine put out 215 HP while the years 1997-98 had 225 HP.
1999-2000 saw another increase to 235 HP, then in 2001 to 2003, the automatic came with 250 HP while the manual transmission was given 275 HP. The torque changed as well and in the end, the company split the torque with the 2001 to 2003 auto transmission having 501 lb-ft and the manual having 525 lb-ft.
The compression held true throughout the run of the Powerstroke engine at 17.5:1
7.3 Powerstroke Cylinder Numbering

It seems that Ford kept this simple for the Powerstroke motor. The passenger side of the engine holds all the odd numbers while the driver’s side holds all the even numbers.
That keeps the confusion away that is created when you say left or right side. On the passenger side, the cylinders are 1-3-5-7 while on the driver’s side it is 2-4-6-8. Nice and simple which makes finding the problem in the cylinders a lot easier.
This order never changed for all the years that Ford made the Powerstroke engine. One of the things you need to be careful of is the change in rods. This engine started out with forged rods and was indicated by the serial number.
But in 2000 the company started p[lacing PMR or powdered metal rods inside the engine. These are not as strong as the forged models. However, sometimes the serial number indicates that the rod is forged but in reality, it is a PMR.
So if you want more information about the engine, do not rely solely on the serial number. Mistakes can be made or substitutions were made for a variety of reasons. PMRs do not have a great reputation.
Ford 7.3 Gas Cylinder Layout

If you look at a chart, you will see that the number 1 cylinder is pushed a little ahead of the number 2 cylinder. That means that the number 8 is bringing up the rear and is slightly behind the number 7 cylinder.
In the following two diagrams, you can see the layout from two different points of view:

And the next one:

Those should give you a very good idea of the layout of the cylinders. There are more complicated images and drawings on the internet you can always look at. A good internet search always seems to produce a good image section that gives you many different perspectives.
Check your manual to see what diagrams or drawings the company provides. Those owner manuals will have some diagrams to help you with any repairs that may come about after you drive your truck for some time.
Ford 7.3 Godzilla Firing Order

Besides the firing order, which only takes one sentence to provide, we will be giving you more information on this engine. The firing order is 1-5-4-8-6-3-7-2. We have double-checked that information.
The 540-pound motor has piston cooling jets and takes 8 quarts of oil. The rocker ratio is 1.8:1 and there is no rocker arm offset. The cylinder heads are made from aluminum while the crankshaft material is forged steel.
Then the piston material is made from Hypereutectic Aluminum and the connecting rods are Powdered Metal, Fractured Cap External Torx Head on Rod Bolts.
The block is made from Iron, Deep Skirt & Siamesed Cylinders and has a bore diameter of 4.22 inches, a 3.976-inch stroke, and a deck height of 9.650 inches. Its bore spacing is 4.530 inches and the thrust bearing location is number 3 main.
The engine is built with a 7.3L or 445 c.I. displacement, it has a compression rating of 10.5:1, 430 HP @ 5500 RPM, and a torque of 475 lb-ft at 4,050 RPM. You will find this motor in the following Ford trucks: F-250, F-350, F-550, F-650, F-750, E-350 & E-450.
This engine was placed in those trucks starting in 2020 and in 2021 it is found in the F-59 Chassis. If you want to identify the engine through its VIN then you need to know that the 8 letter or number is K for all medium and heavy-duty trucks.
The letter N is in the 8th position for all other models. That should give you a good idea of what the Godzilla motor is all about.
Some Final Words
If you are skilled enough to handle your own repairs on these modern engines, then this information should make your work a little easier. Modern engines are tough enough to work on with all the pollution control and fuel efficiency devices attached to modern motors.
Modern engines are not like the old days when you could sit in the engine compartment and do your work very easily. Now you need specialized equipment and tools to do simple repairs and that is never any fun.